
陶器年代区分
唐草の文化史
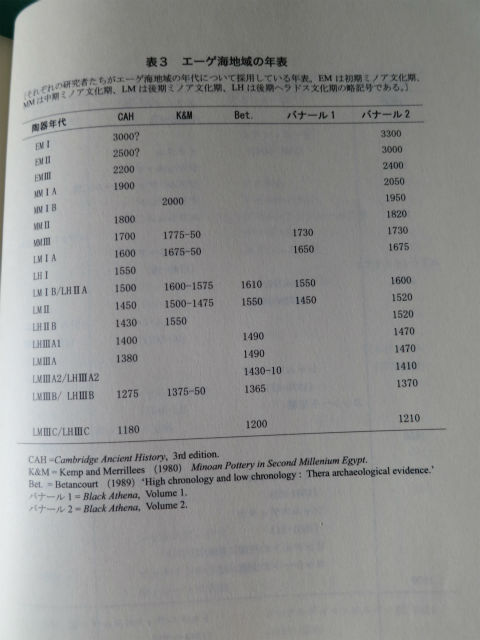
左の列が「陶器年代」
M.バーナルの著書「黒いアテネ」所収の 年表 BC.3300~BC.1210
略号は
EM(初期ミノア文化期)
MM(中期ミノア文化期)
LM(後期ミノア文化期)
LH(後期ヘラドス文化期)
Early Helladic (EH)さらに3区分
Middle Helladic (MH)
Late Helladic(LH)さらに3区分、10区分
| Period | Approximate Date |
|---|---|
| Early Helladic I | 2800-2500 |
| Early Helladic II | 2500-2300 |
| Early Helladic III | 2300-2100 |
| Middle Helladic | 2100-1550 |
| Late Helladic I | 1550-1500 |
| Late Helladic II | 1500-1400 |
| Late Helladic III | 1400-1060 |
| Period | Approximate Date |
|---|---|
| LHI | 1550-1500 |
| LHIIA | 1500-1450 |
| LHIIB | 1450-1400 |
| LHIIIA1 | 1400-1350 |
| LHIIIA2 | 1350-1300 |
| LHIIIB1 | 1300-1230 |
| LHIIIB2 | 1230-1190 |
| LHIIIC (Early) | 1190-1130 |
| LHIIIC (Middle) | 1130-1090 |
| LHIIIC (Late) | 1090-1060 |
| Sub-Mycenean | 1060-1000 |
| Protogeometric | 1000 |
1 Chronology(年表)
1.1 Mycenaean Culture(ミケーネ文化)
1.2 Late Helladic I-IIA (ca.1675/1650 - 1490/1470 BC)後期Helladic I-IIA
1.2.1 Late Helladic I (ca. 1675/1650 - 1600/1550 BC)
1.2.2 Late Helladic IIA (ca. 1600/1550 - 1490/1470 BC)
1.3 Late Helladic IIB-IIIA1 (ca. 1490/1470 - 1390/1370 BC)
1.3.1 Late Helladic IIB (ca. 1490/1470 - 1435/1405 BC)
1.3.2 Late Helladic IIIA1 (ca. 1435/1405 - 1390/1370 BC)
1.4 Late Helladic IIIA2-B (ca. 1390/1370 -1190 BC)
1.4.1 Late Helladic IIIA2 (ca. 1390/1370 - 1320/1300 BC)
1.4.2 Late Helladic IIIB (ca. 1320/1300 - 1190 BC)
1.5 Late Helladic IIIC (ca. 1190-1050/1025 BC)
1.5.1 Early Phase
1.5.2 Developed Phase
1.5.3 Late Phase
幾何学文様: 円 チェッカー 三角形 ジグザグ 蛇行(アート)
鳥 魚 動物(一般的に牛や馬) 人間
パターン: スケール スパイラル 山形 タコ シェル 花
He put forward one of the two systems of relative chronology used by archaeologists for Minoan history. It is based on the development of the architectural complexes known as "palaces" at Knossos, Phaistos, Malia, and Kato Zakros, and divides the Minoan period into Prepalatial, Protopalatial, Neopalatial, and Post-palatial periods. The other system is based on pottery styles, as suggested by Arthur Evans.
![]() ギリシア考古学者のニコラス・プラトンのページには、考古学者が使うミノア年表の2つのうちの一つを作ったという話があった。クレタ宮殿のpre、proto、neo、postの4期。他の一つはアーサー・エヴァンズが示唆した陶器様式によるもの、とある。
ギリシア考古学者のニコラス・プラトンのページには、考古学者が使うミノア年表の2つのうちの一つを作ったという話があった。クレタ宮殿のpre、proto、neo、postの4期。他の一つはアーサー・エヴァンズが示唆した陶器様式によるもの、とある。
One of the hot topics in Minoan archaeology is chronology. There are two sets of Minoan chronology, one which reflects stratigraphic levels in archaeological sites, and one which attempts to plot cultural changes, with an emphasis on the Minoan palaces, since that's the defining characteristic. Traditionally, Minoan culture is divided into events. The chronology starts about 3000 BC; Knossos was founded about 1900 BC, Santorini erupted ca 1500 BC; and Knossos fell in 1375 BC.
However, recent investigations indicate that Santorini may have erupted about 1600 BC, although there is still some question about that; clearly, these absolute dates will continue to be controversial for some time to come. The following chronology is from Yannis Hamilakis' 2002 book, Labyrinth Revisited: Rethinking 'Minoan' Archaeology.
訳:: (
ミノア考古学でホットな話題の一つは年表です。ミノア年表、遺跡の層序のレベルを反映する基準1つ、それは決定的な特徴ですので、ミノア宮殿に重点を置いて、文化的な変化をプロットしようとすると1の2つのセットがあります。伝統的に、ミノア文化はイベントに分割されています。年表は3000年頃に開始されます。クノッソスは、1900年頃に設立されました、サントリーニ島は約紀元前1500年の噴火およびクノッソスは紀元前1375年に落ちた。
しかし、最近の調査は約いくつかの疑問がまだあるものの、サントリーニ島、1600年について紀元前に噴出した可能性があることを示す。明らかに、これらの絶対的な日付が来るまでに時間のために論争であり続けるでしょう。
以下の年表は、
ヤニスHamilakisから"2002[ラビリンス再考:再考"ミノア"考古学」)
初期のミノアI 3300-2900 BC
初期のミノアIIA 2900-2550 BC
初期のミノアIIB 2550-2300 BC
pre宮殿(EM III / MM IA)2300年から1900年BC(Vasilike、ミルトス、Debla、Mochlos)
proto宮殿(MM IIA-MM IIIA)1900年から1700年BC(クノッソス、Phaistos、マリア)
neo宮殿(MMIIIB)1700年から1600年BC(アギアTriadha、Tylissos、Kommos、アクロティリ)
neo宮殿(LM IA-LM IB)1600年から1450年BC(Vathypetro、 Kommos、Palaikastro)
後期ミノアIIIA / B 1450-1200 BC(Kydoniaの)(後半からミノアII Kommos、Vathypetro)
後期ミノアIIIC 1200-1150 BC

![]() ここで「ヘラドス(orへラディック)」を確認しておきます。
ここで「ヘラドス(orへラディック)」を確認しておきます。
en.wuikipediaの記述と
M. バーナルとの違いは、後者はすべての期間をHelladicとし(「本土」中心)、初期Helladicについても、アナトリアの文化モデルの影響The infiltration of Anatolian cultural modelsを大きく言っているように見えるのは先入見であろうか。
ヘラドス文化
世界大百科事典より引用ギリシア本土の青銅器文化。ヘラドスHelladosはギリシアを意味するヘラスにちなむ。ヘラディック文化ともいう。他のエーゲ諸文明に対応して初期,中期,後期に分けられるが,後期はミノス文明の影響のもとに変質し,飛躍的に発達するので,これをミュケナイ文明とよんで区別する。リシアの新石器時代にはテッサリアを中心に特色あるセスクロおよびディミニ土器をもつ文化が発達した。これらは東方からの伝来らしい。前2600年ころになると,やはり東方からの影響と思われるが,青銅器文化がテッサリアを残して中部から南部ギリシアにまで現れる
【エーゲ文明】 《 Aegean civilization 》
前30~前12世紀ころ、エーゲ海で栄えた青銅器文明。はじめ、非アーリア系地中海人によるクレタ文明を中心に展開し、のち、アーリア系民族によるミケーネ文明が主流となった。
http://www2.ocn.ne.jp/~greekart/misc/chrono.html
![]() ※このあたりの記述、M.バナールで「黒いアテナ」が批判するところ《アーリア・モデル》・・であるか、こちらが正統派であろうが・・
※このあたりの記述、M.バナールで「黒いアテナ」が批判するところ《アーリア・モデル》・・であるか、こちらが正統派であろうが・・
また、アメリカ本家の About.comはすごいと思いつつ、
さらに、ミノア文化の年表関連を検索します。
http://ancienthistory.about.com/od/greekarchaeology/g/Mycenaean.htm
The Mycenaeans lived during the late Bronze Age in Greece, from about 1600 to 1200 B.C. They are called Mycenaeans after their capital at Mycenae. The period in which they lived (Mycenaean), in ceramic terms is known as the Late Helladic period. We don't know what happened to the Minoans in Crete, but they seem to have been taken over by the Mycenaeans from the Greek mainland, because after 1500 a new writing dominated Cretan records, Linear B, the language of the Mycenaean
The Minoans were what archaeologists have called the early part of the prehistoric Bronze Age of Greece. Bronze Age Greek civilizations are split by tradition into the Greek mainland (or Helladic culture), and the Greek islands (the Cycladic). Named by Arthur Evans after the legendary King Minos, the Minoans were based on the island of Crete, located in the center of the Mediterranean Sea, with a distinctive climate and culture different from that of the other Mediterranean communities.
Minoansは、考古学者はギリシャの先史時代の青銅器時代の初めの部分と呼ばれているものであった。青銅器時代のギリシャ文明はギリシャ本土(またはHelladic文化)、およびギリシャの島(キクラデス諸島)に伝統的に分割されます。で指定されたアーサー·エヴァンス伝説のミノス王の後、Minoansは、他の地中海地域のものとは異なる独特の風土や文化と地中海の中心部に位置するクレタ島、に基づいていた。
ミケーネ関連の考古学者たち
Sir Arthur John Evans(1851–1941)
Vere Gordon Childe (1892–1957), better known as V. Gordon Childe
Honor Frost (1917–2010)
Manolis Andronicos(1919-1992)
Marija Gimbutas (1921–1994)
Manfred Osman Korfmann (1942— 2005)
![]() 「リーグルを読む」に戻る前に、もう少し陶器年代について関連用語
「リーグルを読む」に戻る前に、もう少し陶器年代について関連用語


